
The annals of the ancient world brim with astonishing ancient history facts.
This era, a vibrant tableau of breakthroughs, innovation, and achievements, gave rise to marvels like Egypt’s majestic pyramids and the intellectual beacon of the Library of Alexandria.
In this article, we will traverse the winding paths of history, unearthing ten extraordinary facts that underscore the grandeur of our ancient ancestors.
From the dawn of civilizations to the echoes of vanished empires, these tales will catapult you into the ancient epochs, providing a unique lens into the remarkable milestones of our predecessors.
So, prepare to delve into a thrilling journey through time and marvel at the spectacular wonders of the ancient world.
10 Interesting Ancient History Facts Listed
As we journey through time to explore the remarkable achievements of humanity’s past, we begin with the birthplace of civilization: Mesopotamia.

1. Ancient Mesopotamia
In the eastern Mediterranean region, Mesopotamia was the “cradle of civilization” and home to several important developments in human history.
One such development was the invention of the wheel, which revolutionized transportation and made it easier to move goods from one place to another.
This innovation profoundly impacted Mesopotamian society, enabling them to build larger cities and expand their trade networks.
Another significant achievement of ancient Mesopotamia was planting the first cereal crops.
The fertile land between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers enabled the Mesopotamians to grow wheat, barley, and millet crops.
This development transformed how people lived, as they no longer had to rely solely on hunting and gathering for food.
Instead, they could settle in one place and cultivate crops, leading to the development of agriculture as a way of life.
In addition to these innovations, Mesopotamia was also home to the development of the cursive script, mathematics, astronomy, and other important fields.
The invention of writing, in particular, was a significant achievement, as it allowed for the preservation of knowledge and the sharing of information across time and space.
The contributions of ancient Mesopotamia have had a lasting impact on human history and have influenced many aspects of modern society.
Having delved into the innovative contributions of Mesopotamia, our journey through ancient history facts now takes us to the sands of Egypt, where the majestic Great Pyramids of Giza stand as a testament to human ingenuity and architectural prowess.
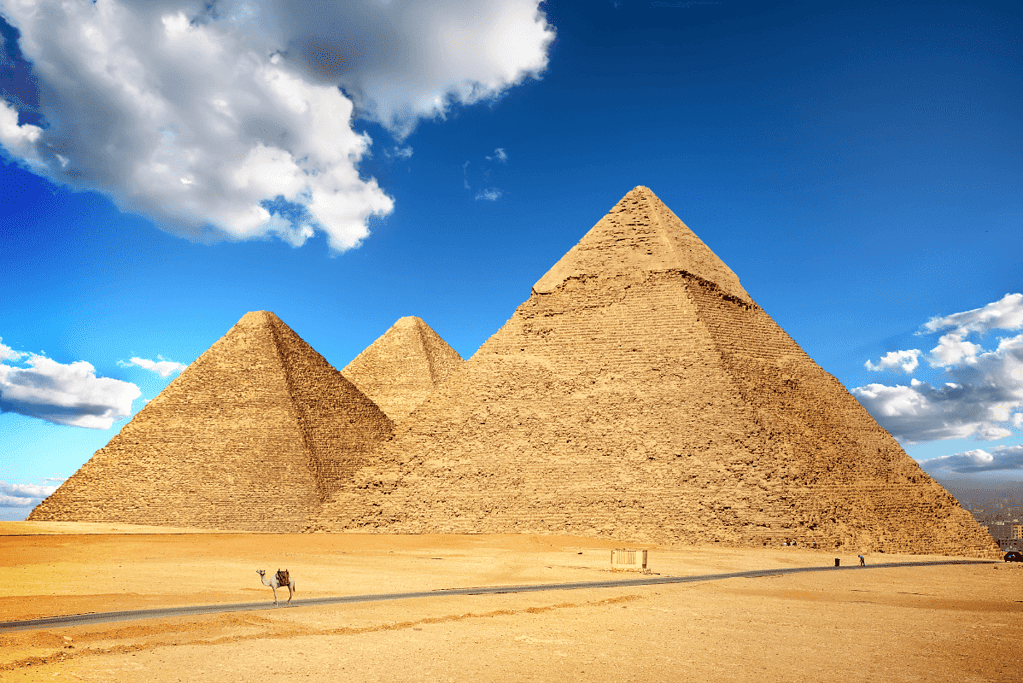

2. Egyptian Pyramids
The Egyptian Pyramids are some of the most iconic structures in the world.
The Great Pyramid of Giza, in particular, is one of the most famous and awe-inspiring structures in human history.
Built around 2580-2560 BC for the Pharaoh Khufu, this pyramid was the tallest man-made structure for over 3,800 years.
The sheer size and scale of the pyramid are truly remarkable, and it remains a testament to the ingenuity and resourcefulness of ancient Egyptian society.
One of the most impressive aspects of the Great Pyramid of Giza is the precision of its construction.
Despite being built thousands of years ago, the base sides of the pyramid only have a mean difference in length of 58 millimeters.
This accuracy level is astounding, especially when you consider the tools and technology that would have been available to the builders at the time.
The precision of the pyramid’s construction is a testament to the skill and dedication of the ancient Egyptians, who created such a magnificent structure using only simple tools and their own ingenuity.
In addition to its impressive size and precision, the Great Pyramid of Giza has many other fascinating features.
For example, the pyramid comprises over 2 million stone blocks, each weighing an average of 2.5 tons.
The pyramid’s interior is also full of hidden chambers and passageways, many of which are still being explored and studied today.
The pyramid’s construction and design have fascinated scholars and historians for centuries, and it remains one of the most remarkable and enigmatic structures in human history.

3. Greek Democracy
Greek democracy is a truly remarkable innovation in human history, one that has had a lasting impact on the world.
Ancient Athens is often regarded as the birthplace of this system of government, which emerged around 508 BC.
Athenian democracy was based on the idea that eligible citizens were allowed to speak and vote in assemblies on most matters of state, such as laws and policies.
This was a radical departure from the monarchies and oligarchies that had dominated the ancient world, where power was concentrated in the hands of a few.
The Athenian democracy was not without its flaws and limitations, however.
For one, not all people were considered “eligible citizens.”
Women, slaves, and foreigners were excluded from participating in the democratic process.
Additionally, the system was heavily reliant on public speaking and oratory skills, which meant that those better at speaking often had more influence than those who were not.
Despite these limitations, the Athenian democracy was a major step forward in terms of political equality and participation, and it paved the way for future democratic movements worldwide.
In conclusion, the Athenian democracy was a remarkable achievement in human history that paved the way for future democratic movements worldwide.
It was based on the idea that eligible citizens were allowed to speak and vote in assemblies on most matters of state, and it represented a radical departure from the monarchies and oligarchies that had dominated the ancient world.
Although the system had its flaws and limitations, it was a major step forward in terms of political equality and participation, and its legacy continues to inspire people today.
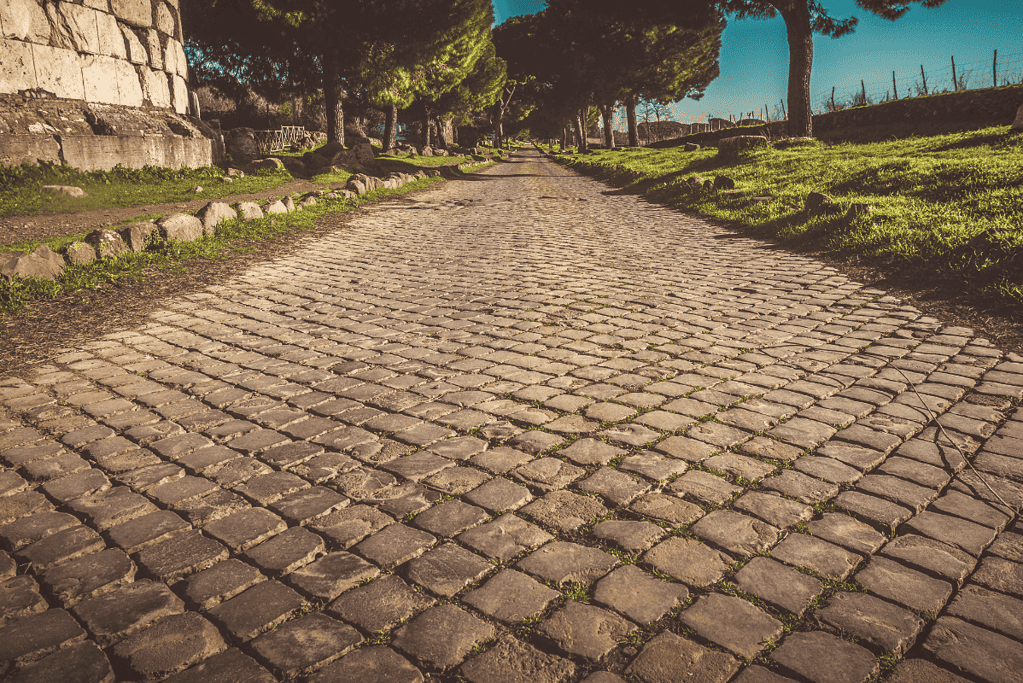

in the ancient Roman Empire, the Appian Way (built circa 312 BC)
4. Roman Roads
The Roman Empire’s vast road network is one of the most remarkable achievements of the ancient world.
The Romans constructed over 250,000 miles of roads, stretching from the British Isles to the Middle East and North Africa to the Danube River.
These roads were primarily built for military use, allowing the Roman army to move quickly and efficiently across the empire and allowing the empire to maintain its vast territories.
The Roman road system was a marvel of engineering, and the roads themselves were a work of art.
The Romans used various materials to construct their roads, including gravel, sand, and lime mortar.
They also used a system of layers to ensure the roads were durable and could withstand heavy traffic.
The bottom layer was made of large stones, followed by smaller stones, and then a layer of gravel. The top layer was made of concrete, which was then covered with a layer of paving stones.
The Roman road system was crucial for the maintenance and growth of the empire.
It allowed for the efficient movement of goods and people, which helped to fuel the empire’s economy.
The roads also allowed for the rapid deployment of troops, which helped the Romans to maintain control over their vast territories.
Today, many of the Roman roads are still visible, and they continue to serve as a testament to the engineering and organizational skills of the ancient Romans.
From the intricately built roads of the Roman Empire that knitted together vast territories, our exploration of ancient history facts now transports us to the hallowed halls of the world’s first libraries, where humankind’s thirst for knowledge was carefully preserved and shared.
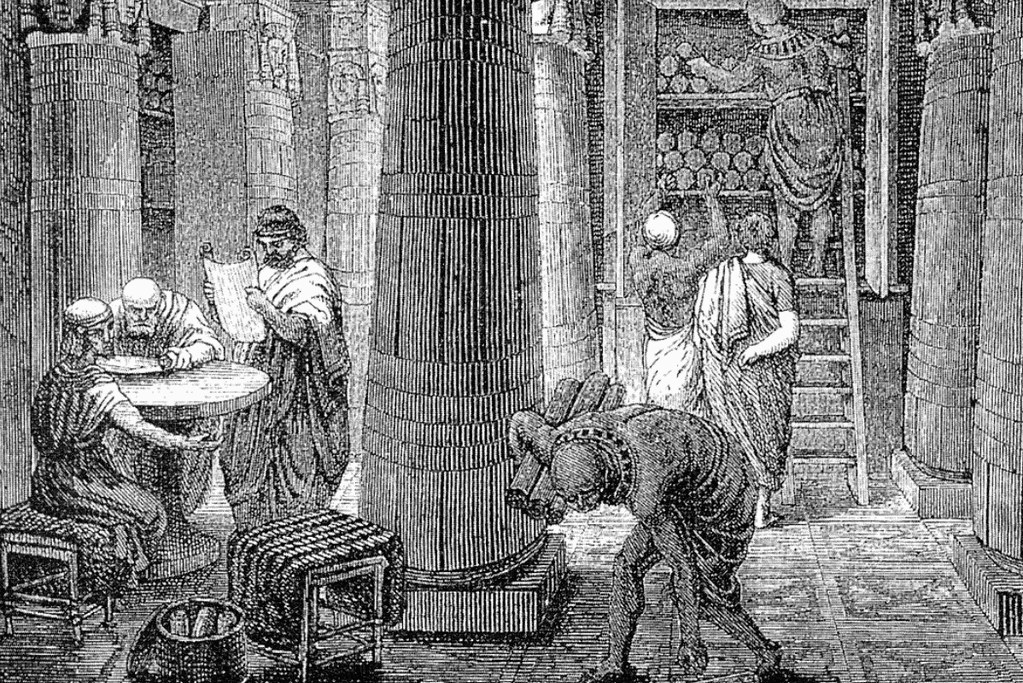
5. The First Libraries
The First Libraries: The ancient world was home to some of the first libraries.
The Library of Ashurbanipal in Nineveh was one of the earliest.
It was built by the Assyrian king Ashurbanipal in the 7th century BC and contained a vast collection of clay tablets inscribed with cuneiform script.
The library was primarily a royal archive containing administrative and legal documents, letters, and scholarly works.
It also included works of literature, such as the Epic of Gilgamesh, which is considered one of the world’s earliest surviving great works of literature.
The library was destroyed by fire in the 7th century AD, but many of its works were copied and preserved in other collections.
However, the most famous ancient library is the Library of Alexandria in Egypt.
Founded in the 3rd century BC by Ptolemy I Soter, the library aimed to collect all the world’s knowledge.
It was a center of scholarship and learning, with scholars from around the world coming to study and conduct research.
The library’s collection was vast, containing hundreds of thousands of papyrus scrolls, including works of literature, science, philosophy, and history.
The library also had a museum, or research institute, where scholars could study and conduct experiments.
Unfortunately, the Library of Alexandria did not survive intact.
It was destroyed in a series of fires and attacks, the most famous being the burning of the library by Julius Caesar in 48 BC.
Despite this, the library’s legacy lived on, as many of its works were copied and preserved in other collections.
The Library of Alexandria remains an enduring symbol of the ancient world’s commitment to scholarship and the preservation of knowledge.
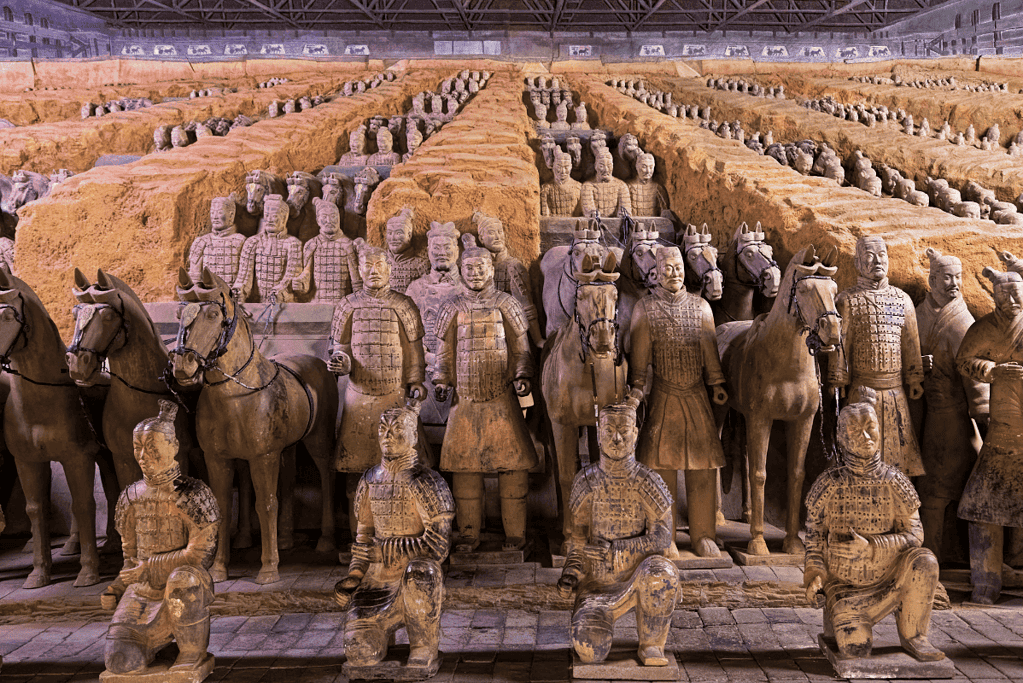
6. China’s Terracotta Army
In 1974, one of the most significant discoveries in the history of archeology was made in China.
The discovery was a collection of terracotta sculptures that depicted the armies of Qin Shi Huang, the first Emperor of China.
The sculptures were found buried with the emperor in 210–209 BC and were designed to protect him in his afterlife.
The Terracotta Army, as it is now known, is a form of funerary art that is considered one of the most extraordinary collections of ancient Chinese art.
The Terracotta Army is made up of thousands of life-sized sculptures that are arranged in battle formation.
The army includes soldiers, horses, chariots, and other military figures, and each one is unique.
The sculptures are made from terracotta, a type of clay fired at high temperatures to create a durable and long-lasting material.
The Terracotta Army is an impressive sight to behold and a testament to the ancient Chinese civilization’s advanced engineering and artistic skills.
The discovery of the Terracotta Army has shed new light on the ancient Chinese civilization and has provided invaluable insights into their culture, beliefs, and traditions.
The discovery has also become a symbol of the power and legacy of the first Emperor of China.
Today, the Terracotta Army is one of China’s most popular tourist attractions, and millions of visitors come to see it every year.
The Terracotta Army is a testament to the enduring legacy of the ancient world and the importance of preserving our cultural heritage for future generations.
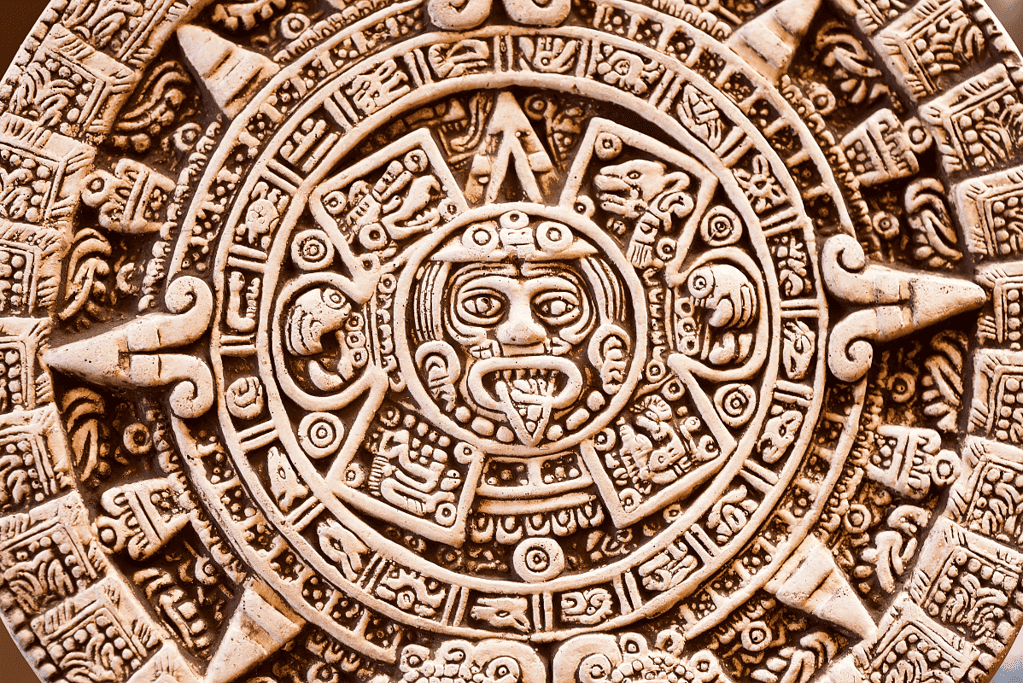

7. Mayan Astronomy
The Mayan civilization was one of the most remarkable civilizations in human history, and their contributions to astronomy were nothing short of extraordinary.
The Mayans were adept at observing the movements of celestial bodies and had a keen understanding of the cycles of the sun, moon, and stars.
Their astronomical observations were critical to their agricultural practices, and they used their knowledge to develop a highly accurate calendar that was more precise than the one used in Europe until the 16th century.
Mayan astronomers studied the movements of the planets and stars and developed highly sophisticated mathematical models to predict their positions in the sky.
They also built impressive observatories to aid their observations, such as the Caracol, a circular tower that provided a 360-degree view of the sky.
The Mayans believed that the movements of the planets and stars were interconnected with human events, and they used their astronomical knowledge to predict the future and make important decisions.
The Mayans’ contributions to astronomy are a testament to their advanced civilization and their dedication to understanding the natural world.
Their astronomical knowledge was essential to their daily lives, allowing them to develop a highly accurate calendar that was more precise than the one used in Europe for centuries.
The Mayan civilization may have declined, but their legacy lives on, and their contributions to science and astronomy continue to inspire us today.
Leaving behind the stellar wisdom of the Mayan astronomers, our voyage through the trove of ancient history facts navigates us to the beginnings of intellectual epicenters, the world’s first universities, where human curiosity and learning found a tangible home.
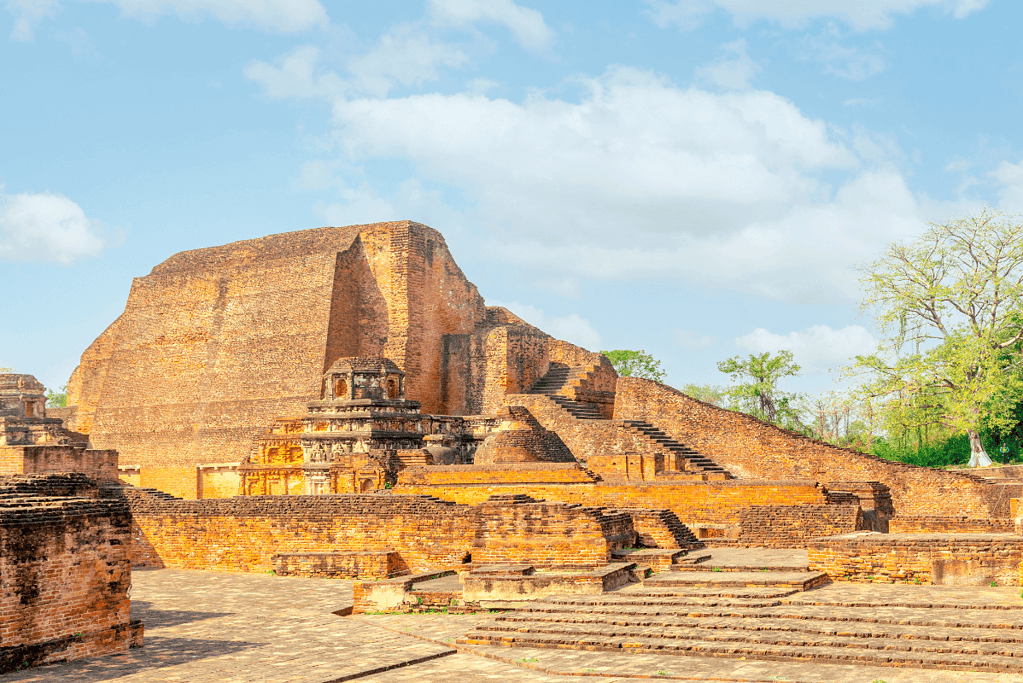

The university operated from about 700 BC to 1193 AD.
8. India’s Ancient Universities
Nalanda University was one of ancient India’s earliest and most renowned learning centers in Bihar.
The university was established during the Gupta dynasty in the seventh century BC and was home to scholars worldwide.
The university was renowned for its curriculum, which included mathematics, astronomy, medicine, and philosophy.
The teachings were based on the ancient Indian scriptures and were delivered in Sanskrit.
Nalanda University was a place of learning and a center for research.
The university had an extensive library, considered one of the largest in the world at that time.
The library had over 9 million books and manuscripts, including works on religion, science, and philosophy.
The university also had a research center where scholars conducted experiments in various fields and significantly contributed to advancing knowledge.
The university peaked during the Gupta and Pala dynasties when it accommodated over 10,000 students and 2,000 teachers.
However, the decline of the university began in the 12th century, when it was attacked and destroyed by Muslim invaders.
The university was rebuilt in the 19th century but was closed again in 1193 when Turkish Muslim invaders destroyed it.
Today, the ruins of Nalanda University are a UNESCO World Heritage Site and a testament to India’s rich history of learning and scholarship.
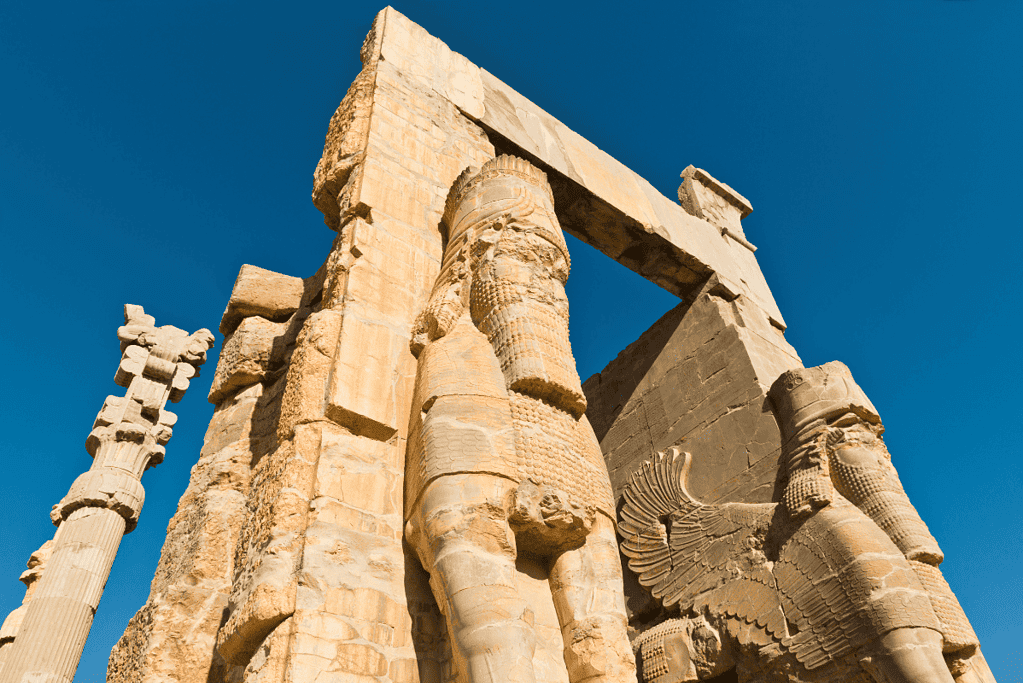

9. Ancient Persian Empire
The Persian Empire was one of the most significant empires in the ancient world, lasting from 550 BC to 330 BC.
It was the largest empire in the world by land area, covering almost 5.5 million square kilometers.
The Persian Empire was ruled by a series of powerful kings, the most famous of whom was Cyrus the Great.
Cyrus was known for his military conquests, but he was also known for his enlightened policies, including his tolerance of different cultures and religions.
Despite their wars with Greece, the Persians were known for tolerating the customs and religions of their conquered lands.
They believed in treating their subjects fairly and respectfully, so they maintained control over such a vast empire for so long.
The Persians were also famous for their impressive infrastructure, including the construction of the Royal Road, which facilitated trade and communication throughout the empire.
Despite their many accomplishments, the Persian Empire eventually fell to the armies of Alexander the Great in 330 BC.
However, their legacy lives on, and their influence can be seen in many aspects of modern Persian culture.
From their impressive architecture to their enlightened policies, the Persians left an indelible mark on the ancient world, and their legacy continues to inspire people around the globe.
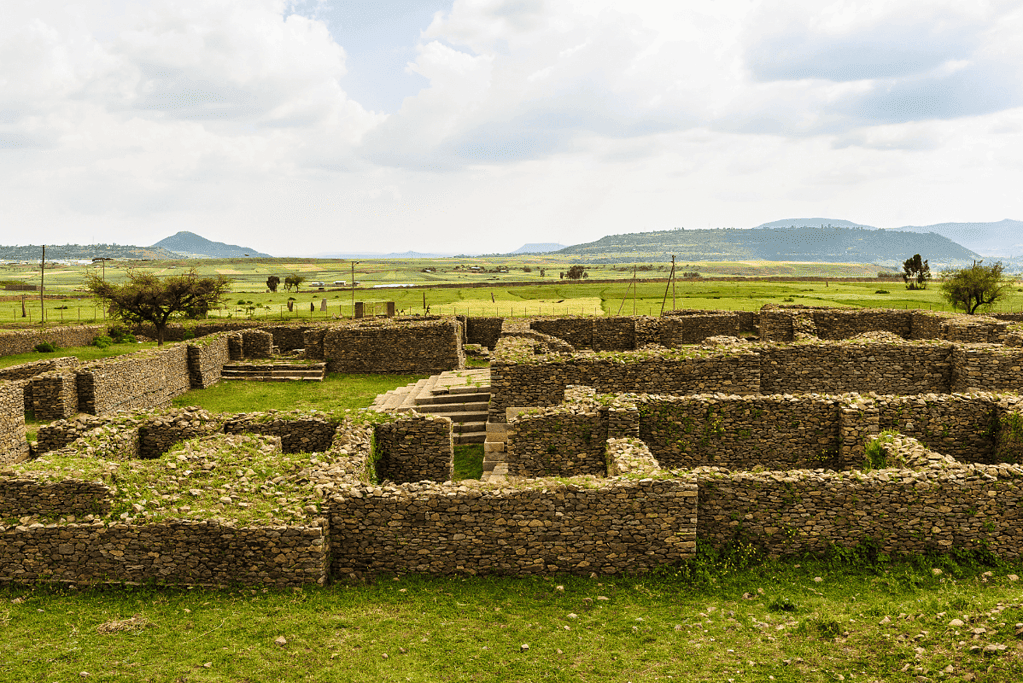

10. African Kingdoms
The Kingdom of Aksum was a powerful and prosperous civilization that emerged in modern-day Ethiopia and Eritrea during the first century C.E.
The kingdom controlled a large territory and dominated trade routes, making it one of the four great powers of its time, alongside Rome, Persia, and China.
The capital city of Aksum was strategically located at the crossroads of trade routes and had lucrative trade partnerships with most of the major states in the known world.
The Aksumites traded in various commodities, including gold, ivory, frankincense, and myrrh, and imported textiles, iron, steel, and weapons.
One of the most noteworthy aspects of the Kingdom of Aksum was its embrace of Christianity.
The kingdom was one of the first major empires to convert to Christianity, adopting the Orthodox tradition of Christianity in the 4th century C.E. under the rule of King Ezana.
This conversion significantly impacted the kingdom’s culture and society, with the construction of elaborate Christian monuments and the spread of Christian beliefs throughout the region.
Aksum’s embrace of Christianity also played a role in its relations with other states, including the Byzantine Empire, which became the kingdom’s key ally.
Despite its impressive achievements, the Kingdom of Aksum eventually declined and was conquered by Muslim armies in the 7th century C.E.
However, the kingdom’s legacy lives on and continues to inspire people worldwide.
Aksum’s cultural and religious heritage, impressive infrastructure, and strategic location have left a lasting impact on the region, and the kingdom remains an important part of Africa’s rich history.
After journeying through the grandeur of the ancient African kingdoms, we draw our exploration of these rich ancient history facts to a close.
Let’s reflect on the profound lessons and insights these remarkable civilizations continue to offer us.
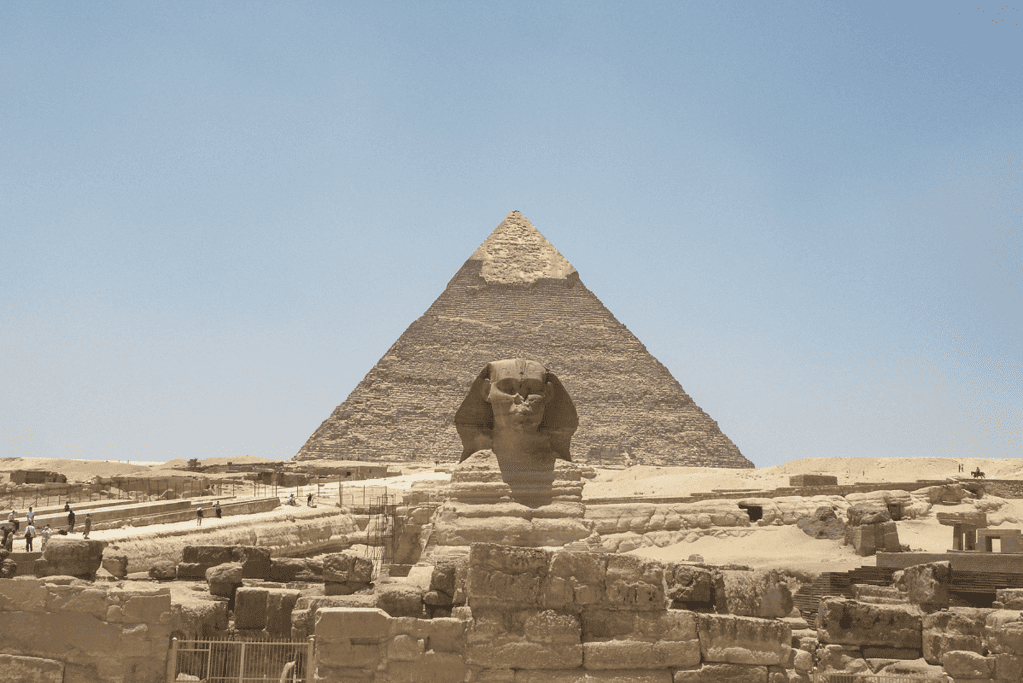

In Closing: 10 Fascinating Ancient History Facts
In conclusion, the ancient world is full of wonders that still amaze us today.
From the grandeur of the Great Pyramids of Giza to the early universities of India, the ancient world has left an indelible mark on human history and culture.
Learning about the past can help us understand the present and inspire us to create a better future.
We hope this article piqued your interest in the ancient world and encouraged you to explore this fascinating period of human history.
Thank you for reading!

FAQs: Ancient History Facts
1. How were the ancient Egyptian pyramids built, given the technology available at the time?
This question has puzzled historians and archaeologists for centuries.
Most theories suggest that it was a massive undertaking involving thousands of workers.
They would have used various tools like copper chisels, wooden wedges, and stone mallets.
Some theories propose that a ramp system was used to drag the large stone blocks into place, but the exact methods remain a subject of ongoing research and debate.
2. What contributed to the fall of the Roman Empire?
The fall of the Western Roman Empire was due to a combination of internal factors and external pressures.
Internally, political instability, economic troubles, and social decay weakened the empire.
Externally, invasions from various barbarian tribes put pressure on the Roman military and economy.
The exact reasons and the process of decline are complex and still widely debated among historians.
3. What was the significance of Nalanda University in ancient India?
Nalanda University was one of the world’s first residential universities, meaning it had dormitories for students.
It was an important learning center, attracting scholars from places as distant as China, Korea, and Central Asia.
The subjects taught there covered various fields of knowledge, including theology, grammar, logic, astronomy, and medicine.
The University is a testament to the high value placed on education and intellectual pursuit in ancient India. Its ruins are now a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
